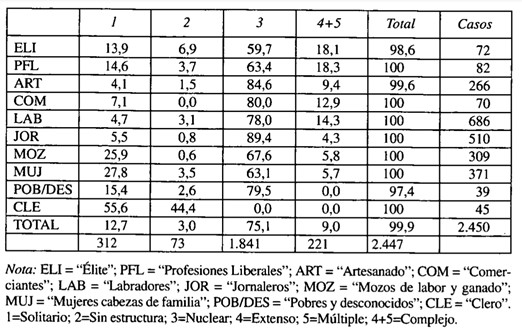
Household structure according to the activities carried out by the head of the household. Occupation determined the composition of the family.
Statistics
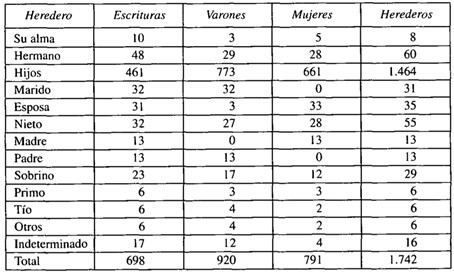
The transmission of wealth through inheritance according to kinship and sentimental affinities. The Castilian model of egalitarian inheritance prevailed, and the most common heirs were the first-born.
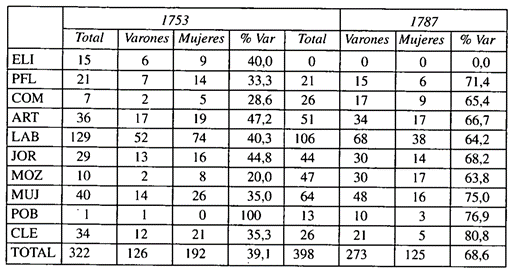
Women heads of household in Spain and the family model they had, highlighting the nuclear family above the rest
Family aggregates over 50 years old within the family nucleus, highlighting the importance of women as cohabitants: mothers and mothers-in-law led the profiles that were most dependent on the household.
Loneliness had a woman’s name. Evolution that shows the survival of customs between the Ancien Régime and liberalism.
Female-headed households in Spain, where widows are the most prominent
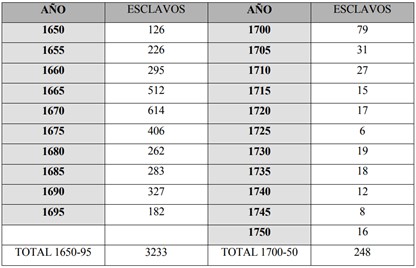
Slave trade in Cadiz according to documentation. Progressive disappearance of this phenomenon.
Economic and commercial growth led to the emergence of a thriving merchant class in Castile. Articulation of trade around the cities.
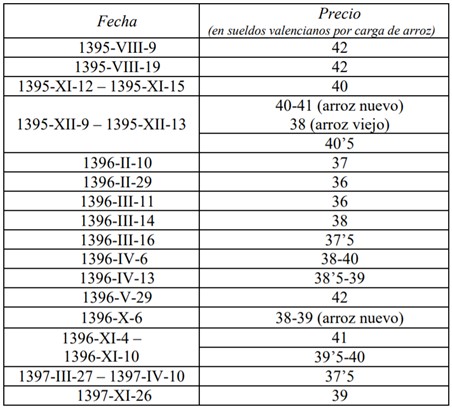
Price fluctuations in the price of Valencian rice explained by climatic, economic and commercial factors.